The fact that comes to mind makes every now and again, when we consider our invulnerable framework, pictures of the fearless white platelets warding off contaminations the main. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) are recognizable among these safeguards as the forefront soldiers. What exactly are PMNs, however, and for what reason would they say they mean a lot to our invulnerable framework guard? This article will plunge into the sorts, capacities, and central positions that PMNs play in staying aware of our prosperity as we research the enchanting universe of PMNs.
What are Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes?
PMNs, or polymorphonuclear leukocytes, are a kind of white platelet perceived by the presence of granular cytoplasm and multilobed centers. These cells are irreplaceable to the safe system since they shield the body from defilement and new gatecrashers.Their cores can seem sectioned or lobed, which is reflected in the name “polymorphonuclear.”
Types of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
PMNs are separated into three essential classes: basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils. Each type adds contrastingly to our resistant protection, with explicit jobs and qualities.
Neutrophils
The most common sort of PMN, neutrophils, every now and again respond to diseases first. They quickly move to contamination locales and, through a cycle known as phagocytosis, immerse and obliterate microbes, assuming a basic part in the natural resistant reaction Additionally, neutrophils release compounds known as antimicrobials, which help in the obliteration of hazardous organic entities. Commonly, these telephones don’t keep going for in excess of several hours or days all at once.
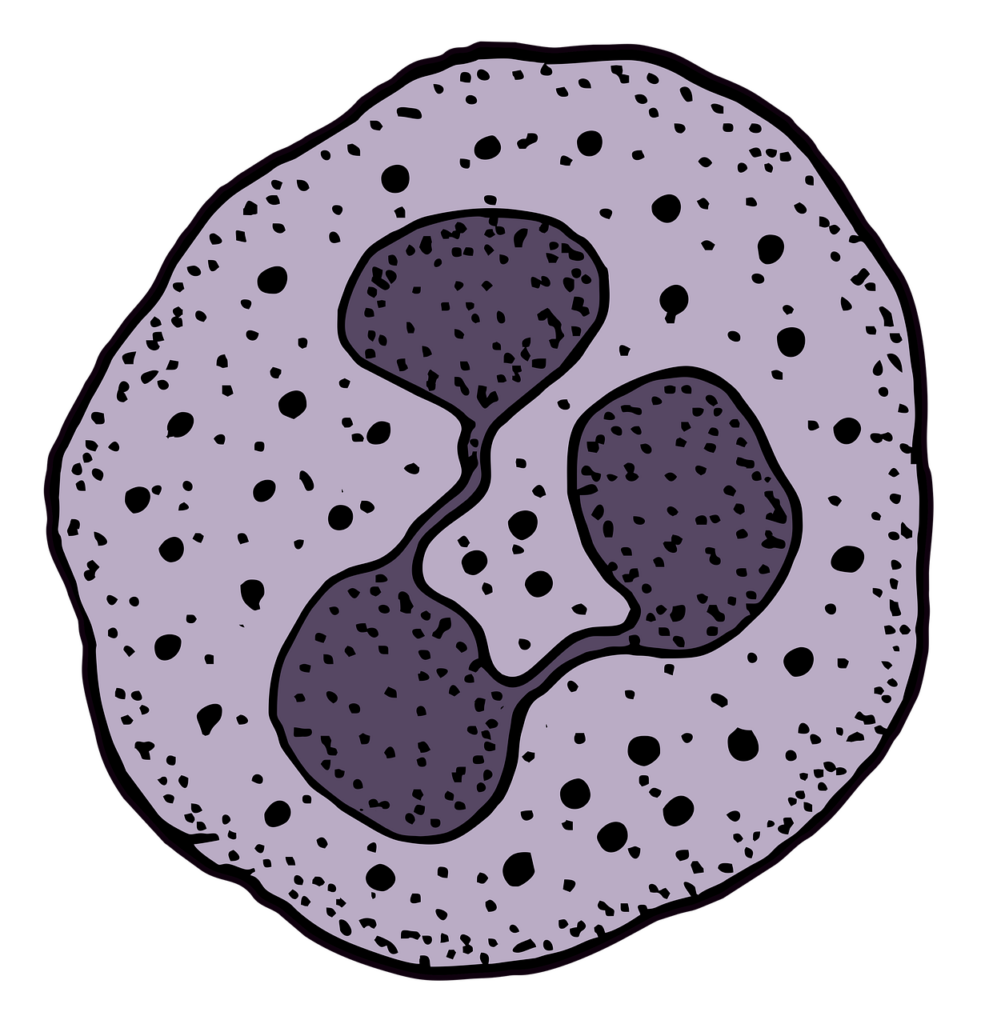
Eosinophils
Eosinophils assume a significant role in unfavorably susceptible responses and asthma, notwithstanding their essential job in battling parasitic contamination. Harmful protein granules inside them can be delivered to kill parasites. By speaking with other safe cells and delivering flagging atoms, eosinophils likewise control fiery reactions. Contingent upon their movement and the requests of the body, their life cycle can endure anywhere from a couple of days to half a month.
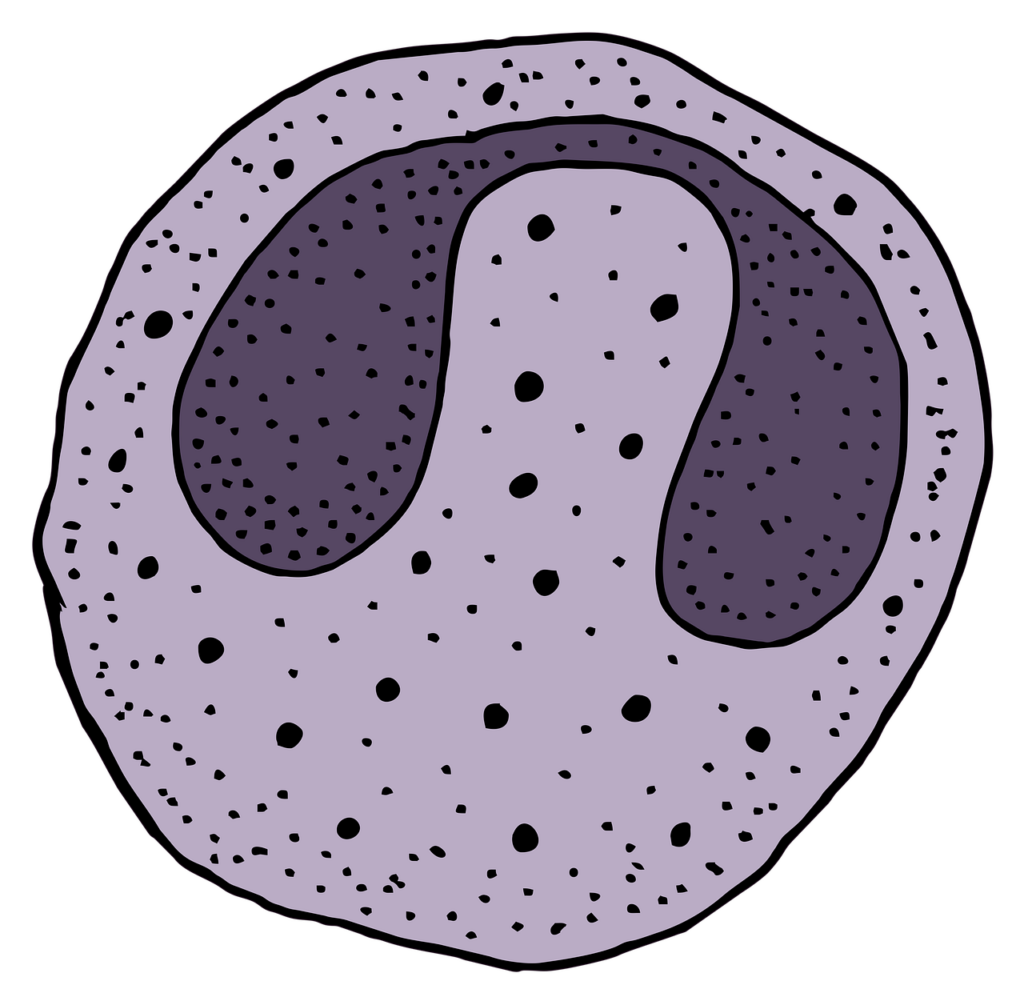
Basophils
The most uncommon sort of PMNs are basophils, which make up under 1% of all white platelets. Since they discharge receptor and heparin, which compound aggravation and cause hypersensitive responses, they are uncommon but significant to the insusceptible reaction. Basophils are engaged in the body’s protection against specific parasites and assume a part in regulating a safe reaction.
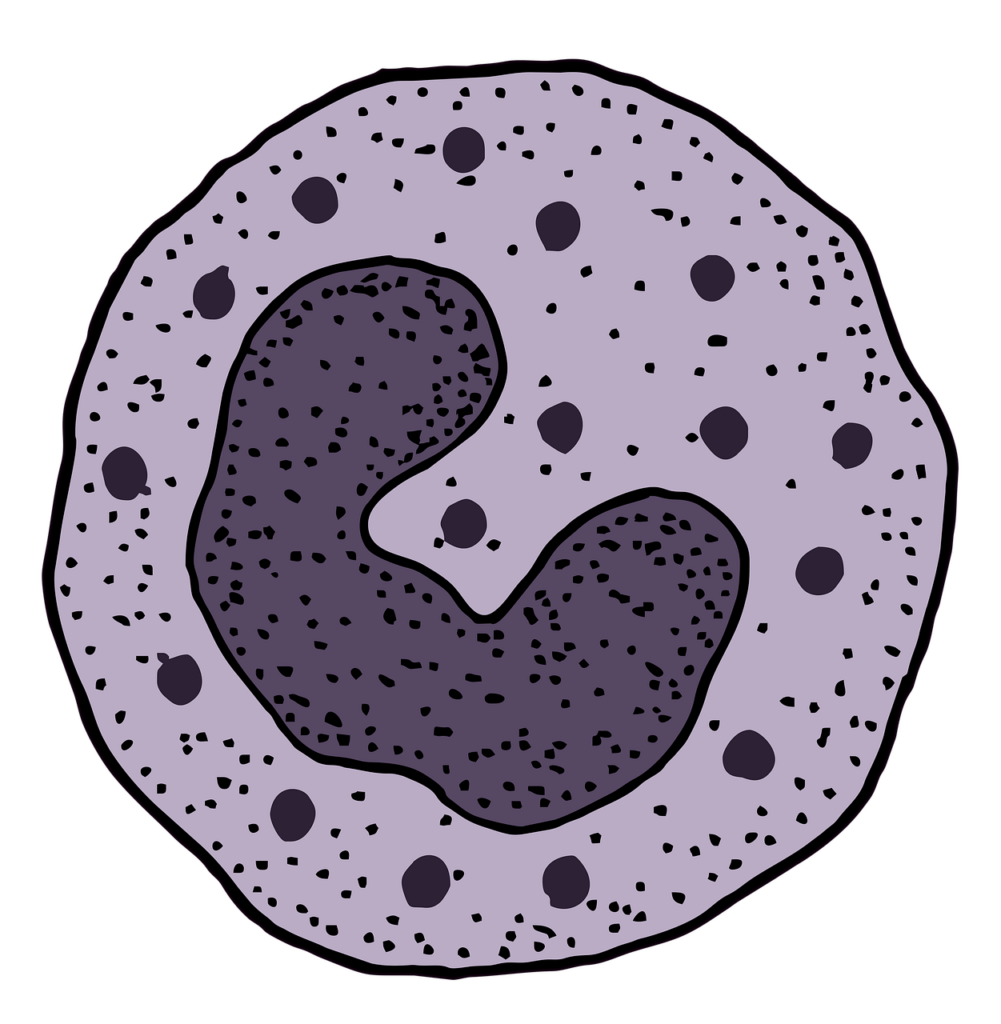
Structure of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
The unmistakable underlying qualities of PMNs set them apart from different kinds of white platelets. The granules of their organic entities contain substances that are poisonous and vital for the obliteration of microorganisms, while their multilobed cores empower them to move through tight spaces inside tissues. The granules can be delegated as essential (azurophilic), optional (explicit), or tertiary (gelatinase) granules, each containing various proteins and catalysts customized for explicit capabilities.
Formation and Development of PMNs
Hematopoiesis is the cycle by which PMNs are made in the bone marrow. The separation of hematopoietic foundational microorganisms into mature PMNs is a convoluted interaction. Among the formative stages are:
- Myeloblasts:are you earliest antecedent cells that bring about PMNs.
- Promyelocytes:intermediatee cells that start to obtain granules.
- Myelocytes:are cells that go through additional separation and granule arrangement.
- Metamyelocytes:are last-stage antecedents that foster sectioned cores.
- Band cells:juvenile neutrophils delivered into the circulation system, which ultimately mature into completely utilitarian PMNs.
Functions of PMNs in the Immune System
PMNs are flexible cells that carry out a few basic roles in the resistant framework:
- Phagocytosis: PMNs inundate and process microorganisms, like microscopic organisms and parasites, through phagocytosis.
- Release of Antimicrobial Substances: They emit chemicals and responsive oxygen species that kill and corrupt microorganisms.
- Inflammatory Response:PMNs are engaged with starting and controlling aggravation, which contains diseases and advanced tissue fix.
Neutrophils: The First Responders
Frequently, neutrophils are the primary insusceptible cells to arrive at the contamination site. Through an interaction known as chemotaxis, they rapidly move to the impacted region, directed by substance signs from other insusceptible cells and harmed tissues. Neutrophils discharge antimicrobial mixtures and phagocytize microorganisms once they show up at the site. Their ability to make extracellular snares (NETs) from proteins and DNA helps with the entanglement and obliteration of microscopic organisms, halting their spread.
Eosinophils: The Allergy and Asthma Fighters
Eosinophils assume a basic role in safeguarding the body against parasitic diseases, like helminth contamination. They likewise assume a part in asthma and unfavorably susceptible responses. Poisonous granule proteins emitted by eosinophils can hurt parasites and fuel irritation. They likewise adjust the insusceptible reaction by associating with other invulnerable cells, including T lymphocytes and pole cells.
Basophils: The Rarest PMNs
Basophils are the most unusual PMNs, yet they are critical to a safe reaction. They discharge receptors, which cause irritation and extend veins. Heparin, an anticoagulant that stops blood thickening at the site of contamination, is additionally delivered by basophils. These cells help guard against parasites and are ensnared in hypersensitive responses.
Role of PMNs in Inflammation
One fundamental part of the safe reaction is irritation, and PMNs are significant entertainers in this cycle. PMNs relocate to the site of disease or injury, discharge supportive cytokines, and attract extra invulnerable cells. This very organized response supports tissue evacuation, disease regulation, and mending. Notwithstanding, perseverance or extreme irritation can cause tissue harm and be a cause of various diseases.
PMNs in Disease and Disorders
PMN-related problems might have significant clinical implications. Low neutrophil counts in a patient with neutropenia raise the risk of contamination. Then again, issues like constant granulomatous illness (CGD) originate from twisted PMNs that can’t annihilate diseases. An expanded eosinophil count, or eosinophilia, is connected to parasitic diseases and sensitivity problems. Grasping these issues requires precise patient analysis and treatment.
Diagnostic Tests Involving PMNs
A few demonstrative tests evaluate PMN capability and count. Normal tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures the number and extent of various white platelets, including PMNs.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: a minuscule assessment of blood to recognize irregularities in PMN morphology.
- Flow Cytometry:is a complex strategy for looking at PMN granule items and surface markers.
Advancements in PMN Research
New revelations and advances in medication are being made because of the continuous exploration of PMNs. The focal point of exploration is creating treatments to regulate the capability of PMNs, grasping their conduct in various illnesses, and examining their role in immune system problems and disease. Designated treatments that can be utilized to one or the other increment or diminish PMN action depending on the situation might actually work on quiet results from here on out.
Lifestyle and Factors Affecting PMN Function
Several lifestyle factors can influence PMN function:
- Diet and Nutrition: For the PMN to work appropriately, a sufficient admission of nutrients and minerals, like zinc and L-ascorbic acid, is required.
- Exercise: Customary activity might work on the invulnerable framework, which incorporates PMN movement.
- Stress: Broadened times of pressure can debilitate the insusceptible framework, which weakens PMNs’ ability to ward off contamination.
- Environmental Factors: Poison and contamination openness can decrease PMN capability and raise the risk of disease.
Conclusion
As the resistant framework’s most memorable line of protection against contamination, polymorphonuclear leukocytes are fundamental. Their ability to immerse microorganisms, respond quickly to dangers, and control irritation makes them fundamental for protecting wellbeing. Appreciating the jobs and elements of PMNs helps with recognizing the complexity and viability of our safe framework. We can expect new revelations and medicines as examination advances, which will work on our ability to fight off ailments and protect ideal wellbeinX
For more, read: Blisterata
FAQs
What are Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes?
PMNs, or polymorphonuclear leukocytes, are a sort of white platelet saw by the presence of granular cytoplasm and multilobed focuses.
What are the main types of PMNs?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are the three essential subtypes of PMNs, and they each play special parts in the resistant framework.
What response do neutrophils need to diseases?
Neutrophils head out rapidly to contamination destinations, discharge antimicrobial specialists, immerse microorganisms by phagocytosis, and make extracellular snares to kill microscopic organisms.
Which part do sensitivities play for eosinophils?
Eosinophils discharge harmful granule proteins that cause irritation and communicate with other resistant cells to alter the reaction, which is the reason they are embroiled in unfavorably susceptible responses and asthma.
Why do basophils matter in the resistant reaction?
Receptor and heparin, which are delivered by basophils and assume an imperative role in irritation and parasite safeguard, increase vein porousness and hinder thickening.