Support hoses, another name for compression socks, are specialty clothing items made to improve blood flow in the lower limbs. These snug socks apply gentle pressure to the legs, reducing blood clotting, inflammation, and symptoms of vein disorders like DVT and varicose veins. Healthcare professionals often recommend knee-high and thigh-high compression options for those who sit or stand for long periods, pregnant women, post-surgery patients, and individuals with circulatory conditions.
Compression Socks: Who Should Wear Them?
Many types of people benefit from compression stockings, such as:
People with Circulatory Problems: Compression stockings are commonly advised for varicose veins, DVT, venous insufficiency, and chronic venous issues to relieve symptoms and enhance blood flow.
Individuals Who Stand or Sit for Long Term: Compression stockings benefit those who have prolonged periods of standing or sitting due to work or daily routines. Compression stockings are recommended for professions like truck drivers, medical personnel, office workers, and others who stand or sit for long periods to prevent blood pooling in the legs.
Women who are pregnant: Increasing pressure on the veins in the legs during pregnancy can cause edema and pain. During pregnancy, compression stockings can aid with leg pain relief, edema reduction, and varicose vein prevention.
Post-Surgery Patients: After surgery, decreased mobility increases the risk of leg blood clots. During the healing phase, compression stockings can help to maintain good circulation and prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Athletes: Athletes, including runners and endurance athletes, wear compression stockings to boost blood flow, reduce muscle soreness, and improve performance during and after exercise.
Overall, compression stockings aid in improving leg blood flow, reducing edema, and easing discomfort from circulatory issues or inactivity. Consult a medical expert to select the appropriate stocking type and compression level.
Compression Socks: How Do They Function?
Compression socks apply gradient pressure, starting at the ankle and decreasing as they move up the leg. They help prevent blood clots by improving blood flow during prolonged sitting or standing. They narrows the diameter of the veins by squeezing the muscles and veins in the legs. This enhances blood flow velocity and keeps blood from collecting in the lower limbs. This enhanced circulation aids in reducing the signs and symptoms of circulatory problems, including weariness, pain, and edema. Compression socks aid in preventing blood clots by improving blood flow, particularly during prolonged sitting or standing.
Types of Compression Stockings
Various kinds of compression stockings are made to fulfill particular purposes. These include:
Stockings with Gradient Compression: These stockings apply graduated pressure, with the most at the ankle and lessening as they ascend the leg. Blood circulation is effectively increased, and blood pooling in the legs is prevented with gradient compression stockings.
TED stockings (Thrombo-Embolic Deterrent), anti-embolism stockings are intended to stop blood clots, especially in patients who are bedridden or have restricted movement. To lower the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), they offer consistent compression throughout the leg.
Medical practitioners prescribe compression stockings to treat a variety of circulation disorders, including lymphedema, venous insufficiency, and varicose veins. Stockings come in different lengths and compression levels, measured in mmHg, including knee-high, thigh-high, and full-length.
Sport Compression Socks: These socks for athletes provide tailored compression to boost blood flow, decrease muscle soreness, and enhance performance. To keep the feet dry and comfortable, they frequently have breathable materials and textiles that drain away moisture.
Maternity Compression Stockings: Specifically made for expectant mothers, maternity compression stockings reduce leg discomfort, edema, and varicose veins. They accommodate the expanding tummy while gently compressing and supporting the legs.
Fashion Compression Stockings: These compression stockings blend therapeutic benefits with stylish patterns, ideal for those seeking leg health with flair. To accommodate a range of tastes and situations, they are available in an assortment of hues, designs, and materials.
Every kind of compression stocking has a distinct function; these include medical applications, improving sports performance, and stylish options. Consult a healthcare provider to select the best type and compression level for your needs.
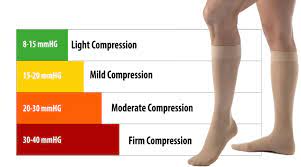
Different Compression Levels for Compression Socks
Compression stockings come in a range of compression levels, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg):
- Low compression: Less than 20 mmHg
- Medium compression: 20-30 mmHg
- Moderate to high compression: 30-40 mmHg
- Firm compression: 40-50 mmHg
Because of the graded compression, which starts at the ankle and gets weaker as it goes up the leg.
The progressive compression aids in rerouting blood flow in the direction of the heart.
Lower compression levels (15–20 mmHg) help relieve moderate leg aches, weariness, and edema and are available over-the-counter.
Prescriptions are usually needed for higher compression levels (20–30 mmHg and above), which are regarded as medical-grade.
The condition and symptoms of the individual determine the proper compression level. Higher compression levels treat severe conditions like varicose veins, DVT, lymphedema, and significant swelling. Mild compression may be appropriate for general leg health and comfort. After an evaluation, a healthcare professional might suggest the appropriate compression level.
Benefits of Compression Socks
Compression socks offer several benefits, including:
Better Circulation
Compression socks, which gently push on the legs, improve blood circulation. Especially helpful for those with circulatory issues like varicose veins, DVT, or venous insufficiency.
Reduction of Symptoms
By reducing discomfort and increasing mobility, compression socks help reduce symptoms like pain, heaviness, weariness, and restless legs that are linked to circulation problems.
Decreased Swelling
Particularly after extended periods of sitting or standing, the compression these socks provide helps minimize fluid buildup in the legs, decreasing swelling and pain.
Prevention of Blood Clots
Compression socks, especially after surgery or during extended periods of immobility, decrease the risk of blood clots by encouraging blood flow and preventing blood from collecting in the legs.
Enhanced Performance
By helping to remove metabolic waste products from the muscles after exercise, compression socks help athletes recover more quickly, increase blood circulation, and lessen muscular soreness.
Support During Pregnancy
Compression socks are beneficial to expectant mothers because they reduce discomfort and leg swelling brought on by the increased pressure on the legs’ veins.
Warmth and Protection
Compression socks can also offer warmth and protection, which makes them appropriate for use in cold weather when engaging in outdoor activities or for people whose work requires them to spend a lot of time in difficult environments.
All things considered, compression socks provide a flexible way to support leg health, enhance comfort, and improve circulation in a variety of situations and applications.
How to choose compression socks
To ensure your compression socks effectively cater to your needs, several factors must be considered. Firstly, the compression level, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), should align with your specific condition and healthcare provider’s recommendations. Higher compression levels are suitable for severe disorders, while milder compression (8–15 mmHg) suffices for mild edema and discomfort.
Secondly, achieving a correct size is crucial for both comfort and efficacy. Consult the manufacturer’s sizing chart and measure your leg length, ankle circumference, and calf circumference. While the socks should fit snugly, they shouldn’t be overly tight or restrictive, and they should adequately cover the problematic area, whether the thigh or calf.
Additionally, consider the length of the socks, ranging from knee-high to thigh-high or full-length stockings. Your preferences and the extent of your condition will dictate the appropriate length. Knee-high socks are generally suitable for most situations, but thigh-high or full-length stockings may be necessary for more comprehensive leg coverage or increased support.
Material is another important aspect, especially if you have sensitive skin or allergies. Look for breathable, moisture-wicking materials such as polyester, spandex, or nylon blends to keep your legs dry and comfortable. Some compression socks also feature antibacterial properties to prevent odor and bacteria buildup.
Furthermore, determine the primary purpose of wearing compression socks—whether for everyday comfort, sports performance, or medicinal reasons. Choose socks specifically designed for your intended use, such as sports compression socks for athletic activities or medical-grade compression stockings for circulatory disorders.
Lastly, consider the aesthetic aspect. While style may not be the primary concern for medical-grade compression stockings, fashion compression socks offer therapeutic benefits alongside fashionable designs, allowing you to express your individuality while promoting leg health.
By considering these factors and consulting with your healthcare professional, you can select compression socks that effectively meet your needs, providing the support and comfort required for optimal leg health.
Compression Stocking Wearing Instructions
For compression stockings to offer the desired comfort and advantages, proper wear is crucial. The following is an in-depth guide on how to wear compression stockings:
Choose the correct size
To begin, determine the compression stocking size that fits you best by using the manufacturer’s sizing guide and your measurements. A snug yet comfortable fit that isn’t overly tight or constrictive is guaranteed by proper sizing.
Prepare Your Skin
Make sure your legs are clean and dry before putting on compression stockings. Lotions, oils, and moisturizers should not be used on your legs, as they may interfere with the stockings’ ability to stay in place.
Turn the Stocking Inside Out
Turn the compression stocking inside out, with the heel facing outward, to make it easier to put on. Make sure the toe area is positioned correctly.
Place Your Foot
After finding a comfortable spot to sit or lie down, carefully place your foot into the compression stocking’s toe. Avoid shoving your foot inside the stocking, as this may tear or injure it.
Pull Up Gradually
Smooth out any creases in your leg as you slowly pull the compression stocking up. To ensure a consistent fit and distribute the fabric equally, use both hands. To keep the stocking from becoming damaged, take your time and don’t rush.
Placement
After the compression stocking has been fully drawn up, make sure your leg is wearing it correctly. The stocking’s heel should press firmly on your heel, and there shouldn’t be any extra material showing where your toes should meet the stocking.
Eliminate All Wrinkles
Look for any bunching or wrinkling of the fabric, especially in the calf and ankle regions. Gently tug and adjust the stocking until it fits snugly and comfortably against your skin, smoothing out any wrinkles.
Repeat the process
Do the same procedure on the other leg if you’re using compression stockings that are knee- or thigh-high.
Verify Fit and Comfort
After placing both compression stockings, make sure they are cosy and evenly compress your legs. To guarantee a good fit and the highest level of comfort, make any necessary modifications.
You can effectively wear compression stockings to benefit from their therapeutic effects and support better leg health by following these measures. See your healthcare practitioner for advice and support if wearing compression stockings causes you any discomfort or problems.

Tips for People Purchasing Compression Stockings for the First Time
Here are some tips for first-time compression stocking users:
Putting on Compression Stockings
- When your legs are less swollen in the morning, put on compression stockings.
- Before you put on the stockings, make sure your feet and legs are clean and dry.
- To make the stockings go on more easily, dab on some talcum powder or baby powder.
- Spread the material evenly across your leg, being careful not to wrinkle or bunch it.
- Rubber gloves, according to some, can improve grip on the stockings and keep them from breaking or tangling.
- The top band of the stocking should never be folded or rolled down, as this can restrict circulation.
Adjusting the Fit
- Make sure the stockings are not overly tight, as this may injure tissue by cutting off the blood flow.
- Make sure the ankle and instep regions are smooth and the toes are not confined.
- Speak with your healthcare practitioner about attempting a lower compression level if the stockings seem too tight.
Wearing and Caring for Compression Stockings
- Usually, compression stockings are taken off at night and worn during the day.
- Regarding how often and how long to wear the stockings, heed your doctor’s advice.
- To maintain the suppleness, hand wash the stockings and hang them to dry.
- Make sure you put on clean compression stockings first thing in the morning.
Monitoring for Issues
- Keep an eye out for symptoms such as discoloration, warmth, cramping, numbness, or swelling in your legs.
- Put the stockings away and speak with your doctor if you encounter any problems.
- To guarantee that the compression stockings are worn correctly and safely, it is important to adhere to the directions given by your physician or vein specialist. Compression stockings can be a useful tool for treating a variety of vein and circulation problems if they are fitted properly and maintained.
Side Effects of Wearing Compression Socks
Although most individuals find compression stockings to be safe and efficient, there are a few possible adverse effects to be aware of:
Skin Irritation
People with sensitive skin or allergies to specific textiles or colors may be more susceptible to skin irritation or allergic reactions to the materials used in compression stockings.
Pain or Discomfort
Excessive pressure or wearing too-tight compression stockings can result in pain, discomfort, or even tingling and numbness in the legs. Ensuring the socks are the correct size and have the appropriate amount of compression is crucial.
Pressure Sores
Extended or ill-fitting compression stockings can put too much pressure on specific skin regions, which can cause pressure sores or ulcers, particularly in people with impaired skin integrity or circulation problems.
Restricted Blood Flow
Rarely, wearing compression stockings for extended periods without taking breaks or with too high compression levels may limit blood flow to the legs, which can result in issues like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clots.
Heat Sensitivity
Compression stockings may make you feel hotter or uncomfortable by retaining more heat in your legs, particularly in warmer weather or after extended physical exercise.
Difficulty Sleeping
If compression stockings are overly tight or the wearer is not accustomed to wearing them, it may be difficult for them to fall asleep.
Difficulty Putting on or Removing
Compression stockings can be difficult to put on and take off, particularly for people with limited dexterity or mobility. This could make you frustrated or make it harder to put on the stockings correctly.
Latex Allergies
People who are allergic to latex or sensitive to it may experience allergic responses when using compression stockings made of latex. It’s critical to examine the materials used in the stockings and, if necessary, choose alternatives devoid of latex.
Exacerbation of Existing Conditions
Wearing compression stockings may occasionally make pre-existing medical disorders worse. Examples of this include peripheral neuropathy and circulation problems. It’s critical to keep an eye out for any worsening of symptoms and to seek medical advice if necessary.
Before wearing compression stockings, you must speak with a healthcare professional, particularly if you have any underlying medical conditions or are worried about any possible adverse effects. When wearing compression stockings, if you feel any uncomfortable side effects, stop using them right away and get medical help.
For more read: How to Get Semaglutide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long is the recommended daily wear for compression stockings?
The length of wear is determined by personal requirements and medical professionals’ advice. While some people wear compression stockings all day, others might only do so when engaging in particular activities or being immobile.
Is it possible to sleep with compression stockings on?
Wearing compression stockings while you sleep may be comfortable for some people but difficult or uncomfortable for others. It’s essential to speak with a healthcare professional to find out if you should wear compression stockings to bed.
Can I use a washing machine to wash compression stockings?
To preserve the suppleness and efficacy of compression stockings, it is normally advised to hand wash them in a moderate detergent and let them air dry. For precise advice, consult the manufacturer’s care instructions.
When you wear compression socks, where does the fluid go?
Tissue fluid is retrieved by the lymphatic circulation and reabsorbed into the bloodstream when compression stockings are worn. It is advisable to use a compression hose in the morning, right before getting out of bed, to reduce swelling. The least amount of edema occurs at this point.
Conclusion
Compression socks are useful clothing that has several advantages for controlling a variety of medical issues, enhancing circulation, and supporting leg health. They help lessen swelling, ease discomfort, and avoid issues like blood clots and varicose veins by applying progressive compression and mild pressure to the legs. They offer a flexible solution accommodating various demands and preferences, be it relieving leg pain, improving athletic performance, or treating circulatory difficulties.

